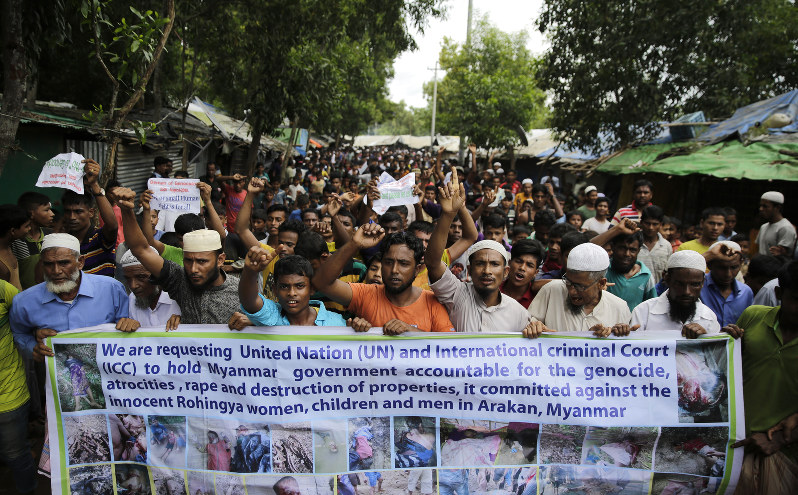
It is important that we understand the causes of such extremism. After all, Islamic extremism was virtually unknown fifty years ago and suicide bombings were inconceivable. And yet today it seems that we are confronted with both on a daily basis.
So what happened to bring Islamic fundamentalism to the forefront of global politics?
While there are many factors involved, undoubtedly one of the primary causes is Western imperialism. Western intervention in the Middle East over the past century to secure access to the region’s oil reserves established a perfect environment in which Islamic fundamentalists could exploit growing anti-Western sentiment throughout the Islamic world with some establishing violent extremist groups. The most recent consequence of this process is the terrorist group known as the Islamic State, which emerged out of the chaos caused by the US invasion of Iraq.
In order to understand the rise of the Islamic State we must first briefly review the history of Western intervention in not only the Middle East but throughout the world to reveal that Islamic extremism in not a unique phenomenon. For the past 500 years, peoples throughout the world have resorted to acts of violence that today would be classified as terrorism in efforts to resist Western imperialism. Indigenous peoples in the Americas often used violent tactics to defend themselves against the brutal European colonizers. There were also many violent slave revolts by Blacks who had been shipped from Africa to the Americas in the service of Western imperialism.
In Southeast Asia, the Filipino people first violently resisted the Spanish and then rose up again when the United States became the new colonial ruler of the Philippines in 1898. Apparently, Washington’s newest colonial subjects didn’t appreciate President William McKinley’s concern for their well-being when he arrogantly declared that since Filipinos “were unfit for self-government, … there was nothing left for us to do but to take them all, and to educate the Filipinos, and uplift and civilize and Christianize them.” Meanwhile, in South Africa, the Zulu people were resorting to violence in an effort to resist British attempts to “civilize” them in the late 1800s. Back then, those who violently resisted Western imperialism weren’t labelled “terrorists,” we just called them “savages.” These are just a few examples of the countless attempts throughout the global South to resist the violent and often brutal expansion of Western imperialism, which included not only the imposition of Western values and culture on people, but also Christianity.
One of the reasons that Islamic extremism has only come to the fore in recent decades is the fact that Western imperialism in the Middle East is a relatively recent occurrence. Western imperialism didn’t begin to make serious headway in the Middle East until the early 20th century. Consequently, we haven’t yet succeeded in our quest to violently subjugate the peoples of that region to the degree that we have peoples throughout most of the rest of the world. In american leech some Middle Eastern nations, Western imperialism initially took the form of traditional colonialism, which involved direct rule. In other countries, it has constituted a neo-colonial approach utilizing international institutions such as the UN Security Council, the International Monetary Fund and the World Bank as well as direct US and European intervention in the forms of military coups and outright war.
While European nations, particularly Britain, had made some inroads into the Middle East in the late 1800s, it was the discovery of oil in Iran in 1908 that marked the arrival of Western imperialism. The London-based Anglo-Persian Oil Company (APOC) gained the rights to Iran’s oil and, because its major shareholder was the British government, Britain effectively controlled Iran’s oil sector. During the ensuing decades there were major protests by the Iranian people who were unhappy with foreign ownership of the country’s oil and the fact that Iran was receiving only 16 percent of its own oil wealth. In 1950, the Iranian parliament finally responded to popular demands and voted to nationalize the country’s oil sector. The following year, Prime Minister Mohammed Mosaddegh established the National Iranian Oil Company.
Unhappy with Iran’s decision to claim ownership of its own oil resources and to use them for the benefit of the Iranian people, the United States and Britain orchestrated a coup to oust the moderate, secular and democratically-elected Mosaddegh government. Shah Reza Pahlavi was installed in power and the new pro-Western dictator immediately re-opened the door for Western companies to return to Iran. And to ensure that the Shah maintained iron-clad control over the population, the United States provided him with military aid as well as training for his secret police force, which would brutalize the Iranian people for the next 26 years.
Under the Shah, Western oil workers flooded into Iran and the country’s capital Tehran became a decadent playground for high-paid foreign oil workers who engaged openly in un-Islamic activities including alcohol consumption, casino gambling and prostitution. And while the country’s oil wealth was flowing into the pockets of foreigners and the Shah and his cronies, most Iranians were struggling to survive in poverty. Not surprisingly, Islamic fundamentalists began pointing to Western imperialism and Western decadence as an affront both to Islam and to the Iranian people. It was a narrative that began to resonate with many impoverished Iranians who had traditionally been moderates. In 1979, under the leadership of the Ayatollah Khomeini, a popular revolution overthrew the Shah’s repressive regime and established an Islamic state.
Reflecting on the US role in Iran, former US Secretary of State Madeleine Albright stated, “In 1953 the United States played a significant role in orchestrating the overthrow of Iran’s popular Prime Minister Mohammad Mosaddegh. The Eisenhower Administration believed its actions were justified for strategic reasons; but the coup was clearly a setback for Iran’s political development. And it is easy to see now why many Iranians continue to resent this intervention by America in their internal affairs.”
The first significant success for Islamic fundamentalism directly resulted from the United States and Britain overthrowing a democratically-elected and secular government and their subsequent support for a brutal dictatorship, all in the name of securing access to oil. Today, we are not only still dealing with the consequences of this Western imperialism in our relations with Iran, but also with Iran’s support for other fundamentalist groups in the region such as Hezbollah.
The same year that Iran became an Islamic state, the Soviet Union invaded Afghanistan to defend that country’s unpopular Soviet-backed regime from a growing insurgency. The mujahideen rebels, like the Islamic revolutionaries in Iran, were fighting against a Western-backed dictatorship. This time it was the atheist communists of the Soviet Union that were the imperialists. The Soviet invasion of Afghanistan only boosted the strength of the mujahideen as recruits flocked from throughout the Islamic world to help liberate the country from the foreign infidels. Many of the tens of thousands of recruits came from Saudi Arabia, which contributed to the fundamentalist movement known as Wahhabism expanding from being a fringe sect of Islam that primarily existed in Saudi Arabia to a major religious force throughout the Sunni Islamic world.
The United States viewed the Soviet occupation of Afghanistan through a Cold War lens and began providing weapons and training to the Islamic fundamentalist mujahideen rebels. During the 1980s, Washington supplied the mujahideen with $4 billion in arms that significantly strengthened the fundamentalists and President Ronald Reagan publicly referred to them as “freedom fighters.” One of the mujihadeen beneficiaries of US aid was a Saudi named Osama bin Laden. The primary objective of the war for this particular “freedom fighter” was the removal of a Western military from Islamic lands. The mujahideen succeeded in their holy war in 1989 when the Soviet Union withdrew its forces. And then, in 1996, following a civil war between various factions of the mujahideen, the recently-formed Taliban emerged victorious and established a fundamentalist government.
As a 1993 article in the British daily Independent made clear, Osama bin Laden was viewed by the West as a warrior, not a terrorist, for his role in the mujahideen. The article, titled “Anti-Soviet Warrior Puts His Army on the Road to Peace,” described bin Laden’s work building roads in the impoverished nation of Sudan in the early 1990s. But bin Laden was not only building roads, he was also establishing a new organization with his mujahideen fighters that would eventually be called al-Qaeda. The mission of al-Qaeda essentially remained the same as that of the mujahideen in Afghanistan: to drive Western military forces out of Islamic lands. This time the target was US troops based in Saudi Arabia and Kuwait following the first Gulf War. Consequently, bin Laden went from being a “freedom fighter” to a “terrorist” virtually overnight even though his mission hadn’t changed, only the target.
From the perspective of Washington, bin Laden was a “freedom fighter” when he was fighting against the Soviet military presence in Afghanistan but was a “terrorist” when he fought against the presence of US military forces in the Islamic world. From the perspective of bin Laden and his Islamic extremist followers, however, nothing had really changed. Whether it was Soviet soldiers or US troops, both constituted Western military forces that had to be removed from Islamic soil.
Ultimately, Western intervention in the Islamic world gave birth to al-Qaeda. First, Soviet military support for a puppet regime in Afghanistan, then US backing of the Islamic fundamentalists who constituted the mujahideen rebels, and, finally, the establishment of US military bases in Saudi Arabia and Kuwait during the first Gulf War. As a consequence of these imperialist actions, Islamic extremists in the form of the Taliban and al-Qaeda emerged as powerful forces with the latter feeding off the growing disenchantment among Muslims angry at Western militarism in the Islamic world, Western backing for corrupt governments in the Middle East, and US support for Israel and its illegal occupation of Palestinian territories.
Following al-Qaeda’s terrorist attacks against New York City and Washington, DC on September 11, 2001, the United States launched its war on terror and targeted the Islamic extremist group in Afghanistan. However, the Bush administration also sought to exploit the 9/11 attacks to justify ousting Saddam Hussein from power in Iraq. Top Bush administration officials launched a massive propaganda and misinformation campaign to convince the American people that Hussein was directly involved in the 9/11 attacks and linked to al-Qaeda, both of which were untrue. They also portrayed Hussein as a terrorist threat because he possessed weapons of mass destruction, which was another lie.
As the reports by UN weapons inspectors had made clear, Iraq no longer possessed any chemical or biological weapons; they had been destroyed in accordance with UN Security Council resolutions following the first Gulf War in 1991. Furthermore, the Bush administration’s propaganda campaign conveniently ignored the fact that the weapons of mass destruction that Iraq had possessed and used during the 1980s were supplied to it by the United States when Hussein was an ally against the fundamentalist regime that had come to power in Iran.
In March 2003, President George W. Bush ordered the US military to invade Iraq without authorization from the UN Security Council and in direct violation of international law. Four days before the invasion, Vice-President Dick Cheney declared, “From the standpoint of the Iraqi people, my belief is we will, in fact, be greeted as liberators.” But one year later an extensive nationwide poll in Iraq showed that 71 percent of Iraqis saw the US troops as “occupiers” rather than “liberators.” Such a response should not have been surprising given that some 100,000 Iraqis had been killed as a result of the invasion and occupation.
The military occupation gave rise to an insurgency that sought to oust the foreign occupying troops. Prior to the US invasion there had been no Islamic extremist groups operating in the country. But the emergence of the broad-based insurgency and the post-invasion chaos opened the door for al-Qaeda to enter Iraq. And it was out of both the insurgency and al-Qaeda that the fundamentalist Islamic State (originally known as the Islamic State of Iraq and Syria, or ISIS) emerged in 2006.
Following the invasion, the United States dismantled Saddam Hussein’s military and many of the unemployed former officers ended up joining the insurgency. Some of these military officers conspired with a breakaway faction of al-Qaeda in Iraq to form the Islamic State. The new extremist group sought to establish an Islamic caliphate in northern Iraq and Syria. The Syrian civil war in 2011 allowed the Islamic State to cross into Syria where it grew dramatically stronger and began to consolidate control over territory. It then re-focused its efforts on Iraq and easily defeated the new US-trained Iraqi army and consolidated its control over northern parts of that country in 2014. Meanwhile, the West’s military intervention in Libya in 2011 helped turn that country into a failed state and opened the door for the Islamic State to establish a foothold in that part of North Africa.
The Islamic State has had significant success recruiting disenchanted Muslims from around the world to join its ranks and to carry out terrorist attacks in Western nations such as France and Belgium. Last year, even former British Prime Minister Tony Blair acknowledged “there are elements of truth” in claims that the invasion of Iraq led to the creation of the Islamic State. As Blair admitted, “Of course, you can’t say those of us who removed Saddam in 2003 bear no responsibility for the situation in 2015.”
Once again, Western imperialist actions in the Middle East had given rise to Islamic extremism. But the rise of the Islamic State should not have come as a surprise to anyone. That the Bush administration’s illegal invasion of Iraq laid the foundation for the emergence of the Islamic State was entirely predictable. After all, the West’s ouster of the moderate and secular Mosaddegh and its backing of the Shah’s ruthless regime in Iran had given birth to that country’s Islamic fundamentalist revolution. And Washington’s military support of fundamentalist rebels in Afghanistan and its establishment of military bases in Saudi Arabia and Kuwait ensured the emergence of al-Qaeda.
Meanwhile, Western imperialism in other parts of the Middle East over the past century has also contributed to the rise of Islamic fundamentalism. While most of the Arab states in the region gained independence following World War Two, the United States and Britain essentially handed over most of Palestine to European Jews so they could create the Jewish state of Israel. And, ever since, Israel has received unconditional US support to brutally repress the Palestinian people and to repeatedly violate international law, which has generated widespread anti-Western sentiment throughout the Middle East. It wasn’t until after almost 40 years of Israeli rule over Palestinian lands that Islamic fundamentalism and the tactic of suicide bombing finally made inroads among the traditionally moderate Palestinian population. This occurred when Hamas was formed in the Occupied Territories in the mid-1980s. Similarly, it was Israel’s US-supported invasion of Lebanon that gave birth to the fundamentalist group Hezbollah during the same decade.
Over the past one hundred years, the Middle East has been targeted by Western imperialism in the violent manner that the rest of the world has endured for centuries. Nowadays we use politically correct terms such as “democracy promotion” and “human rights” instead of “civilize” and “Christianize,” but they essentially mean the same thing because they are simply the latest justifications for stealing resources and imposing Western values on other cultures. Not surprisingly, as has been the case throughout the rest of the world over the past 500 years, there is widespread resentment and anger towards the West for its imperialist policies in the Middle East. And, also not surprisingly, some fundamentalist Muslim resisters to Western imperialism have resorted to extreme tactics.
Finally, perhaps one of the most disturbing aspects of Western imperialism in the Islamic world is the fact that each consequence has been more extreme than the previous one. Al-Qaeda and the Taliban were far more extremist than the Islamic government that came to power in Iran. And the Islamic State is even more extremist than al-Qaeda. Which begs the question: What new and even more extremist monstrosity are we currently creating with our ongoing military interventions and imperialist policies in the Islamic world?
By Garry Leech, an independent journalist and author of numerous books including How I Became an American Socialist (Misfit Books, 2016), Capitalism: A Structural Genocide (Zed Books, 2012); Beyond Bogota: Diary of a Drug War Journalist in Colombia (Beacon Press, 2009); and Crude Interventions: The United States Oil and the New World Disorder (Zed Books, 2006). ). He also teaches international politics at Cape Breton University in Nova Scotia, Canada and Javeriana University in Cali, Colombia. For more information about Garry’s work, visit garryleech.com
Related :

.jpg)